
Upgrading to and Verifying Magento Community Edition and Enterprise Edition—Part 2
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Upgrade Roadmaps
- Getting Ready For Your Upgrade
- Upgrading the File System, Solr, and Database
- Running the URL Redirect Script EE 1.13.0.0 and 1.13.0.1 only
- Completing the Magento Upgrade
- Testing the Magento Upgrade
- Setting Magento File System Permissions and Ownership After Upgrade
- Troubleshooting
Overview
This article discusses how you upgrade to:
- Magento Community Edition (CE) 1.8 or 1.9.x
- Magento Enterprise Edition (EE) 1.13.0.2, 1.13.1, or 1.14.x
Because of changes to URL rewrites, the following upgrades are more complex than other upgrades.
- Upgrading from EE 1.12 or earlier to EE 1.14.x
- Upgrading from EE 1.13.0.0 or EE 1.13.0.1 to EE 1.14.x
Upgrade Roadmaps
- High-level roadmaps for upgrading to EE 1.13.0.2 or later are discussed in Understanding the Upgrade to EE 1.13.0.2 or EE 1.14.
- To upgrade from EE 1.13.0.2 to EE 1.13.1.0 or later (including EE 1.14.x), see Getting Ready For Your Upgrade.
- To upgrade to CE 1.8 or 1.9, see Upgrade Roadmap for CE 1.8 or 1.9
Getting Ready For Your Upgrade
This section discusses how to get ready for your upgrade by backing up the database and customizations on the file system. The steps that follow do not affect your current production system. You can continue serving customers with no downtime.
To get ready for your upgrade:
- Get the Magento installation archive as discussed in Getting Magento CE or EE.
- Install Magento in a different directory:
- Recommended. Set up a new system (that is, another host) on which to install Magento.
The system should be identical to, if not better than, your current system. The new system must meet the Magento system requirements. - Install Magento in a new, empty root installation directory on the same server.
 Important: Do not upgrade Magento in the same directory on the same server because post-upgrade errors are likely to occur.
Important: Do not upgrade Magento in the same directory on the same server because post-upgrade errors are likely to occur. - Recommended. Set up a new system (that is, another host) on which to install Magento.
- Magento strongly recommends you observe the following guidelines when you set up the Magento database in your development environment:
- Magento for the first time uses MySQL database triggers to improve database access during reindexing. Magento does not support any custom triggers in the Magento database because custom triggers can introduce incompatibilities with future Magento versions.
- Familiarize yourself with these potential MySQL trigger limitations before you continue.
- If you use MySQL database replication, Magento does not support MySQL statement-based replication. Make sure you use only row-based replication.
- Review the MySQL recommendations for MySQL password security.
- Complete the tasks discussed in the following sections in the order shown:
Pre-Upgrade Tasks For Your Production Environment
Complete the tasks discussed in the following sections in the order shown:
- Enabling Exception Logging
- Disabling cron jobs (EE 1.13.0.2 or later)
- Setting All Indexers for Update on Save
- Flushing the Cache
- Backing Up the Database
- Archiving Customizations and Extensions
- Restoring Configuration Settings
Enabling Exception Logging
Before you start your upgrade, you should enable exception logging so it will be enabled on the development system. Without exception logging, it will be more difficult to diagnose errors during your upgrade. You can disable exception logging after you've exported the Magento database.
To enable exception logging:
- Log in to the Admin Panel as an administrator.
- Click System > Configuration.
- In the ADVANCED group, click Developer.
This enables you to enable exception logging so you'll see exceptions in the development environment after the upgrade. - In the right pane, click Log Settings to expand it.
The following figure shows an example.
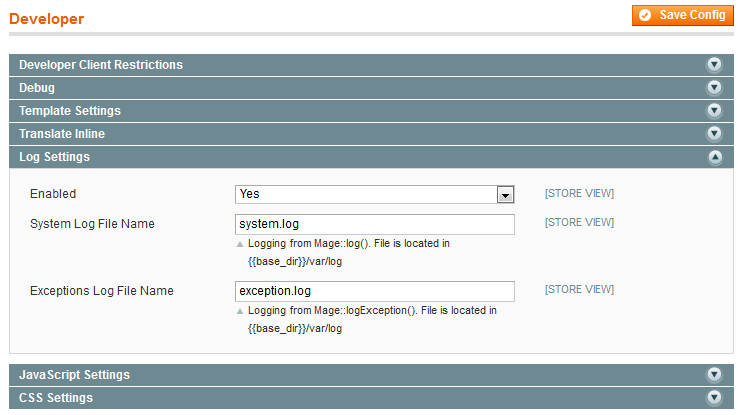
- From the Enabled list, click Yes.
- Optionally change the names of the log files.
- Click Save Config.
Disabling cron Jobs
Before upgrading to EE 1.13.0.2 or later, disable all running cron jobs. A simple way to stop cron jobs follows; consult an appropriate reference for other options.
As a user with root privileges, enter one of the following commands:
- Ubuntu:
service crond stop - CentOS:
service cron stop
Setting All Indexers for Update on Save
This section applies to upgrading Magento EE only. Skip this section if you're using Magento CE.
Because of the changes to indexing in Magento EE 1.13, you must set all indexers to update on save before you upgrade; otherwise, unpredictable performance will result. You can revert indexer settings after you've exported the Magento database.
To set indexers to update on save:
- Click System > Index Management.
- On the top left corner of the row, click Select All to select all indexers.
- From the Options list, click Change indexing mode.
The Index Mode list displays. - From the Index Mode list, click Update on Save.
The following figure shows an example.
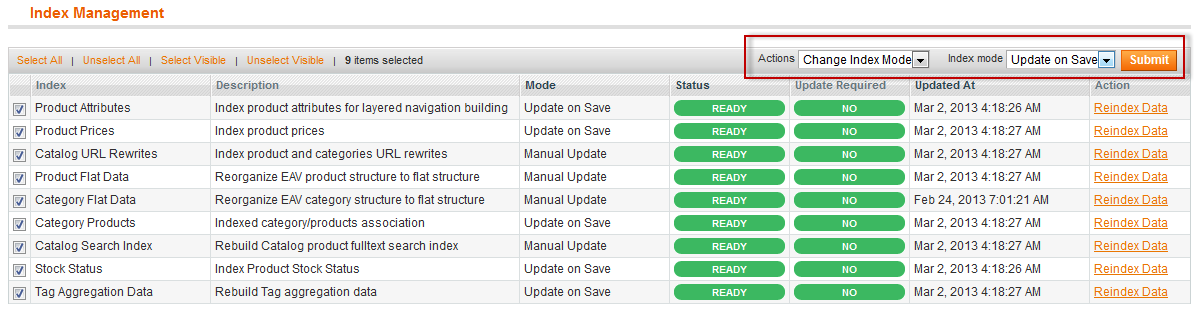
- At the top right corner, click Submit.
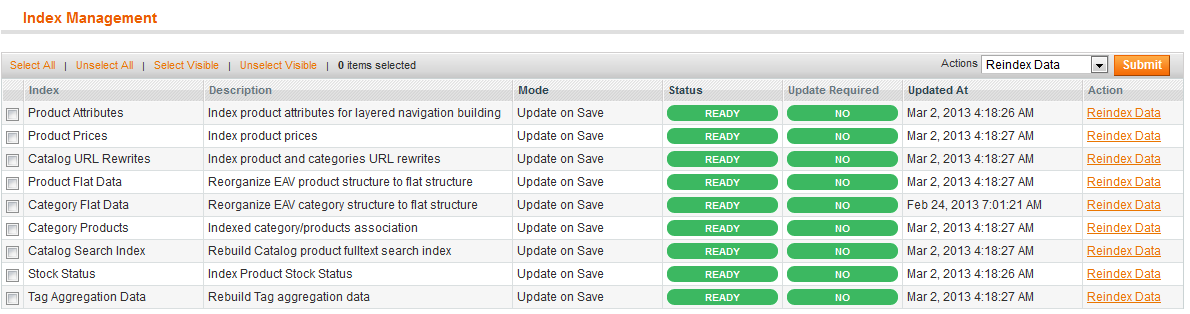
- Make sure all indexers are now set for Update on Save as the following figure shows.
Flushing the Cache
Clear the Magento cache as follows:
- Log in to the Admin Panel as an administrator.
- Click System > Cache Management.
- Click Flush Magento Cache.
Backing Up the Database
Back up your database using mysqldump or another tool. mysqldump syntax follows:
mysqldump -u root magento-database-name > export-file-name.sql
Archiving Customizations and Extensions
To archive your custom themes and extensions:
- Archive the Magento
mediadirectory and all subdirectories. For example,
cd [your Magento install dir] tar -czf media.tgz media
- Archive any custom themes in the following directories:
[your Magento install dir]/app/design/frontend [your Magento install dir]/skin/frontend
- Archive any customizations or extensions in the following directories:
[your Magento install dir]/app/code/local [your Magento install dir]/app/code/community
- Transfer the archives you just created to the development environment.
- Copy
[your Magento install dir]/app/etc/local.xmlto your development environment.
Restoring Configuration Settings
After you've exported the Magento database and extensions, you can revert the configuration changes you made as discussed in these sections:
Pre-Upgrade Tasks For Your Development Environment
In your development environment:
- If necessary, create a Magento installation master directory; Magento installs in a
magentosubdirectory of that directory.
The Magento installation archive creates amagentosubdirectory so if you want your Magento installation directory to be/var/www/magento, you don't need to do anything.
 Tip: The name and path to the Magento installation directory in your development system does not have to be the same as on your production system, although it might make some tasks simpler.
Tip: The name and path to the Magento installation directory in your development system does not have to be the same as on your production system, although it might make some tasks simpler. - Create a new database instance. For example, you can create a new MySQL database instance named
magentousing the following commands:
mysql -u root -p
Enter the remaining commands at themysql>promptcreate database magento; GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO magento@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'magento'; GRANT ALL ON magento.* TO magento@localhost;
For MySQL versions later than 5.0.2 but earlier than 5.1.6, the following command is required:GRANT SUPER ON *.* TO 'magento'@'localhost';
Exit the MySQL command shell:exit
Verify the database exists using the following command:mysql -u magento -p magento
If an error displays, repeat the commands. If the command succeeded, enterexitto return to the command prompt. - If you're using Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux) and Apache must initiate a connection to another host, you must run the commands discussed in this step.
- To determine if SELinux is enabled, use the following command:
getenforce
Enforcingdisplays to confirm that SELinux is running. - Enter one of the following commands:
CentOS:setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect=1
Ubuntusetsebool -P apache2_can_network_connect=1
- To determine if SELinux is enabled, use the following command:
Optional: Upgrading to PHP 5.4
PHP 5.3 is currently the latest PHP version available in the default repositories for Ubuntu and CentOS. PHP 5.3 works with CE 1.8, CE 1.9, EE 1.13, and EE 1.14.
We recommend PHP 5.4 for all of the preceding CE and EE versions because of the new features and changes in that release.
CE 1.8 and EE 1.13 both require a PHP 5.4 patch. The patch is listed as PHP 5.4 Compatibility in the EE support portal.
Upgrading to PHP 5.4—Ubuntu
Use the instructions on phpave.
Upgrading to PHP 5.4—CentOS
Enter the following commands in the order shown as a user with root privileges:
cd /tmp rpm -Uvh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm rpm -Uvh http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/remi-release-6.rpm yum --enablerepo=remi install httpd php php-common
The following resources are also available:
Upgrading the File System, Solr, and Database
Upgrade your Magento installation by completing all of the following tasks in the order shown:
- Upgrade Requirements
- Upgrading Assets on the Magento File System
- Upgrading the Magento Database
- Upgrading Solr (EE 1.14.0.0 only)
- Finishing the File System
Upgrade Requirements
Before attempting your Magento upgrade, complete all the tasks discussed in:
Upgrading Assets on the Magento File System
This section discusses how to extract the Magento archive in your development system and manually copy over your customizations, themes, and extensions.
- Make sure the CE or EE installation archive is located in the directory above where you want Magento to be installed.
For example, to install Magento to/var/www/magento, copy the archive to/var/www. - Extract the archive. For example,
tar -zxf archive-name
This installs Magento CE or EE on the file system on your development system. Next, you'll overwrite some of these assets with customizations from your production system. - Extract the production system's
mediaarchive, overwriting the installation archive. You created themediaarchive as discussed in Getting Ready For Your Upgrade.
 Tip: Copy the media archive to the same level in the directory structure to simplify the process. For example, if you created the media archive on your production system in your Magento install directory, the archive when extracted creates the
Tip: Copy the media archive to the same level in the directory structure to simplify the process. For example, if you created the media archive on your production system in your Magento install directory, the archive when extracted creates the mediadirectory and all subdirectories. If you copy the media archive to the Magento installation directory on your development system, extracting it automatically replaces existingmediasubdirectory contents. - If necessary, move the
mediadirectory and subdirectories tomediadirectory in your new Magento installation, overwriting the existing contents. - Extract the custom theme package archive you created as discussed in Getting Ready For Your Upgrade.
- If necessary, move the theme packages to the
[your Magento install dir]/app/design/frontendand[your Magento install dir]/skin/frontenddirectories, as appropriate, overwriting the existing contents. - Extract the customization and extension archives you created as discussed in Getting Ready For Your Upgrade.
- If necessary, move the extensions and customizations to the
[your Magento install dir]/app/code/localand[your Magento install dir]/app/code/communitydirectories, as appropriate, overwriting the existing contents.
Updating the Magento Database
This section discusses how to:
- Import the production database data into the development database instance.
- In the development database instance, change the values of the paths
web/unsecure/base_urlandweb/secure/base_urlin thecore_config_datatable to the development server's IP address or hostname.
Import the production database data using your database manager tool.
mysql syntax follows:
mysql -u root -p database-name < database-export-filename.sqlFor example, if the database name is
magento and the database export file name is mangento-db-export.sql, enter
mysql -u root -p magento < mangento-db-export.sql
The following sections discuss how to change the base URL paths from http://prod.example.com to http://dev.example.com using SQL commands and phpmyadmin:
- Updating the Base URL the Database Using SQL Commands
- Updating the Base URL the Database Using phpmyadmin
Updating the Base URL the Database Using SQL Commands
This section discusses how to update the secure and unsecure URLs of your webstores and store views in the Magento database. The following example assumes you have two URLs, which every Magento installation has by default. Depending on your setup, you could have more (for additional store views, Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and so on.
Use the following procedure to update all matching URLs in the database.
To update the database with the development system's base URLs using SQL commands:
- Log in to the database server as any user.
- Enter the following commands in the order shown:
mysql -u root -p
Enter the remaining commands at the mysql> prompt.use magento-db-name; SELECT * FROM core_config_data WHERE path LIKE '%base_url%';
- In the resulting output, make note of the rows that include
web/unsecure/base_urlandweb/secure/base_url.
In particular, you must know the value of theconfig_idfor these rows. - Carefully examine the entire URL to avoid mistakes.
- Enter the following command to update the values of
web/unsecure/base_urlandweb/secure/base_url:UPDATE core_config_data SET value='base-url' WHERE config_id=id1 or config_id=id2;
Example 1—config_idsare the same: if your base URL ishttp://dev.example.com/, theconfig_idof the row containingweb/unsecure/base_urlis 354 and theconfig_idof the row containingweb/secure/base_urlis 355, enter:UPDATE core_config_data SET value='http://dev.example.com/' WHERE config_id=354 or config_id=355;
Example 2—config_idsare different: Same as preceding example except thatweb/secure/base_urluseshttps://UPDATE core_config_data SET value='http://dev.example.com/' WHERE config_id=354; UPDATE core_config_data SET value='https://dev.example.com/' WHERE config_id=355;
- Verify the values are set correctly.
SELECT * FROM core_config_data WHERE path LIKE '%base_url%';
- For other URLs, be careful to perform the replacement correctly.
For example, store view base link URLs resemble the following:
http://prod.example.com/view1/
Make sure to update the URL like the following:UPDATE core_config_data SET value='http://dev.example.com/view1/' WHERE config_id=377;
- When you're done, run the following command again:
SELECT * FROM core_config_data WHERE path LIKE '%base_url%';
- If the values are set correctly, enter
exitat themysql>prompt and continue with Finishing the File System.
If not, repeat the tasks discussed in this section. Do not continue until the database is updated.
Updating the Base URL the Database Using phpmyadmin
This section discusses how to use phpmyadmin to change the values of the paths web/unsecure/base_url and web/secure/base_url in the core_config_data table to the development server's IP address or hostname.
- In a web browser's location or address field, enter
dev-web-server-host-or-ip/phpmyadminFor example, if your web server address ishttp://dev.example.com, enterhttp://dev.example.com/phpmyadmin - Log in as the MySQL
rootuser. - In the left navigation bar, click the name of your Magento database.
- In the left navigation bar, click the core_config_data table.
- At the top of the page, click the Search tab.
- In the Search tab page, from the Operator list, click LIKE.
- Enter
%base_url%in the Value field.
The following figure shows an example.

- Click Go.
The following figure shows sample results.
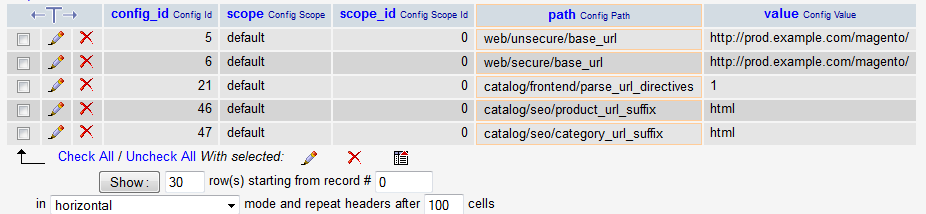
- Click
 (Edit) in the row that includes the path
(Edit) in the row that includes the path web/unsecure/base_url. - Change the value to the hostname or IP address of your development server.
The following figure shows an example.

- Click Go.
- Repeat these tasks for the path that includes
web/secure/base_url. - Exit phpmyadmin.
Upgrading Solr (EE 1.14.0.0 only)
This section applies to upgrading to EE 1.14.0.0 using the Solr search engine only. If you're upgrading to a different version—or if you're not using Solr—skip this section and continue with Finishing the File System.
Because of changes to the Solr schema, you must copy two files from Magento to your Solr installation. Failure to do so might prevent products from displaying on your web store. After copying the files, you must also reindex the catalog search index.
To update Solr:
- If the Solr search engine is running, stop it.
- Copy the following files from the Magento 1.14.0.0 installation to the equivalent directory on your Solr installation:
[your Magento install dir]/lib/Apache/Solr/conf/schema.xml [your Magento install dir]/lib/Apache/Solr/conf/solrconfig.xml
For example, if Magento is installed in
/var/www/html/magentoand the example Solr configuration is installed in the/etc/solr/apache-solr-3.6.2/example/solr/confdirectory on the same host, enter:cp /var/www/html/magento/lib/Apache/Solr/conf/solrconfig.xml /etc/solr/apache-solr-3.6.2/example/solr/conf cp /var/www/html/magento/lib/Apache/Solr/conf/schema.xml /etc/solr/apache-solr-3.6.2/example/solr/conf
- Restart Solr.
- After you copy the files, you must update the catalog search index. To update the catalog search index, open a command prompt window.
- Change to the
shellsubdirectory of your Magento installation directory.
For example, on CentOS:cd /var/www/html/magento/shell
- Enter the following command:
php indexer.php --reindex catalogsearch_fulltext
Finishing the File System
This section discusses how to edit copy local.xml and set file system permissions and ownership on the production system.
Copying local.xml
- Copy your production system's
local.xmlto[your Magento install dir]/app/etc. - Open
local.xmlin a text editor. - If necessary, change the database connection information in the
default_setupelement, as follows:<default_setup> <connection> <host><![CDATA[change-if-necessary]]></host> <username><![CDATA[change-if-necessary]]></username> <password><![CDATA[change-if-necessary]]></password> <dbname><![CDATA[change-if-necessary]]></dbname> <initStatements><![CDATA[SET NAMES utf8]]></initStatements> <model><![CDATA[mysql4]]></model> <type><![CDATA[pdo_mysql]]></type> <pdoType><![CDATA[]]></pdoType> <active>1</active> </connection> </default_setup>
- Save your changes to
local.xmland exit the text editor.
Setting File and Directory Ownership and Privileges
Magento recommends the following ownership and privilege settings for files and directories in the Magento installation directory:
- The Magento installation directory and all subdirectories are owned by the web server user.
This enables the web server to change files in these subdirectories but other users cannot access them (except a higher-level user such asroot). - All directories have 700 permissions (
drwx------).
700 permissions give full control (that is, read/write/execute) to the owner and no permissions to anyone else. - All files have 600 permissions (
-rw-------).
600 permissions mean the owner can read and write but other users have no permissions.
Note: The way you set permissions and ownership depends on whether Magento is running on a dedicated or hosted system:
- Hosted: A Magento server located on a hosting provider. A hosted system typically does not enable you to elevate to
root. The web server typically runs as an ordinary user. Magento assumes you log in as this user to start and stop the web server and that you already own all the files and directories in the Magento installation directory. You can usechmodto change permissions on files and directories. - Dedicated: A Magento server you control and operate. Unlike a hosted system, you can elevate to
rootand, asroot, you can use thechownandchmodcommands to set ownership and privileges in the Magento installation directory.
To set privileges and ownership:
- Log in to your Magento server.
- Change to your Magento installation directory:
#Ubuntu example cd /var/www/magento #CentOS example cd /var/www/html/magento
- Dedicated Magento server only. Enter the following command to set ownership of the Magento installation directory and all its subdirectories:
chown -R web-server-user-name .
For example, on Ubuntu where Apache usually runs aswww-data, enterchown -R www-data .
- Enter the following commands to set directory permissions to 700 and file permissions to 600:
find . -type d -exec chmod 700 {} + find . -type f -exec chmod 600 {} +
Running the URL Redirect Script (EE 1.13.0.0 and 1.13.0.1 only)
If you're upgrading to EE 1.14 from EE 1.13.0.0 or 1.13.0.1, see EE 1.13.1.0 Upgrade: Running the EE 1.13.0.0 or EE 1.13.0.1 URL Redirect Script now. When you're done, return here to continue your upgrade.
Completing the Magento Upgrade
To complete the upgrade, go to your Magento base URL in a web browser. The first time you go to your Magento base URL, server-side scripts run to update the database. Depending on the amount of data in your database, this process can take a long time.
If you're upgrading from a version earlier than CE 1.4 or EE 1.7, Magento strongly recommends the two-step upgrade approach discussed in Upgrade Path. In addition, you should expect the upgrade and testing process to take a long time and to expect more downtime for your production system.
Complete the following tasks in the order shown:
- Running the Upgrade Scripts and Fixing Exceptions
- Running the URL Redirect Script (EE 1.12.x and earlier only)
- Post-Upgrade Tasks (EE 1.13.0.1 Only)
- To apply the security patch released in October, 2016, see How to Apply the SUPEE-8788 Patch.
- Setting Up the Magento Cron Job
- Clearing Magento var/ Subdirectories
- Verifying the Status of Indexers
- Testing the Magento Upgrade
- Taking Your Old Production System Offline
Running the Upgrade Scripts and Fixing Exceptions
The first step in your upgrade is to run server-side upgrade scripts. Depending on the nature of your customizations and extensions, and how many customers and products are in your database, these scripts can take a long time to run and can result in exceptions. You must resolve all exceptions before continuing to the next step in the process.
This step in the upgrade process is iterative; that is, you'll probably run through it more than once.
To run the upgrade scripts:
- In a web browser address or location field, enter your Magento installation's base URL.
(You updated the Magento database with the development system base URL as discussed in Updating the Magento Database.) Note: If you upgraded Magento on the same server, you might need to update your Apache web server's virtual host configuration to reference the new Magento installation directory. For more information about configuring virtual hosts, see the Apache Virtual Host documentation.
Note: If you upgraded Magento on the same server, you might need to update your Apache web server's virtual host configuration to reference the new Magento installation directory. For more information about configuring virtual hosts, see the Apache Virtual Host documentation. - Wait while upgrade scripts run on the server.
- If fatal errors or exceptions display in the browser, they are most likely related to customizations. To resolve fatal errors, you must:
- Analyze the errors to determine the root cause.
You can find errors in the web server's error log or in[your Magento install dir]/var/log. - Fix the cause in your extension code.
- In your development environment, drop the Magento database.
- Re-create the development database and import production data into it as discussed in Updating the Magento Database.
- Use the following command to delete the contents of the Magento
var/subdirectories:rm -rf [your Magento install dir]/var/cache [your Magento install dir]/var/full_page_cache \ [your Magento install dir]/var/locks [your Magento install dir]/var/session
 Note: Some of these directories might be empty; this is normal.
Note: Some of these directories might be empty; this is normal. - Clean up the file system as discussed in Finishing the File System.
- Repeat step 1 in this section.
- Repeat the tasks discussed in this section until no more fatal errors display in the browser.
- Analyze the errors to determine the root cause.
Post-Upgrade Tasks (EE 1.13.0.1 Only)
This section applies to upgrading from 1.13.0.1 only. If you're upgrading CE or if you're upgrading from a different EE version, continue with Setting Up the Magento Cron Job.
After successfully running the Magento upgrade and fixing errors, enter the following command from the Magento root directory:
php -f shell/indexer.php -- --reindexall
This command runs a full reindex and it might take a long time, depending on the size of your database.
After the reindex completes, enter the following command from your Magento installation directory:
rm -rf var/cache var/full_page_cache var/locks
Continue with Setting Up Magento Cron Jobs.
Running the URL Redirect Script (EE 1.12.x and Earlier Only)
If you're upgrading to EE 1.14 from EE 1.12 or earlier, see EE 1.14 Upgrade: Running the EE 1.12 and Earlier URL Redirect Script now. When you're done, return here to continue your upgrade.
Setting Up the Magento Cron Job
You should now set up your Magento cron job as discussed here.
Clearing Magento var/ Subdirectories
Run the following command to clean the Magento var/ subdirectories:
rm -rf [your Magento install dir]/var/cache [your Magento install dir]/var/full_page_cache [your Magento install dir]/var/locks
Verifying the Status of Indexers
After the cron job runs, all indexers should be in a Ready status. Before testing your upgrade, verify all indexers are Ready; otherwise, your testing will be inconclusive.
To verify the status of indexers:
- Log in to the Admin Panel as an administrator.
- Click System > Index Management.
Verify that all indexers have a status of Ready, as the following figure shows.

- If indexers are not Ready, use the following guidelines:
Indexer status Suggested action Scheduled Wait for cron to finish or run http://magento-host-name/cron.phpfrom a web browser.Processing Wait for cron to finish or run
cron.phpfrom a web browser. (For example,http://www.example.com/magento/cron.php)If indexers are Processing for an extended period of time, run the command discussed in Clearing Magento var/ Subdirectories and refresh the Index Management page.
Testing the Magento Upgrade
After you have upgraded with no fatal errors or exceptions, Magento strongly recommends you thoroughly test the upgrade in your development environment as follows:
- Test all extensions and customizations thoroughly.
Make sure the UIs perform as expected, make sure the extensions behave properly, and so on. - Run some orders, making sure prices are calculated correctly and that orders go through the configured payment mechanisms.
- If you encounter issues, get help.
- Before making the development system live, back up everything in your production and development environments again.
The way you make your development system live is up to you; a simple way is to update your DNS server to point to the development IP address.
Taking Your Old Production System Offline
The last step in upgrading is to take your production system offline and switching to your development system—which then becomes the production system from that point on.
To switch from your production to development system:
- Put your production system in maintenance mode so it cannot accept orders or other changes.
To do so, create an empty file named[your Magento install dir]/maintenance.flag. - Test it by going to your Magento web store's front page.
The following message displays if you set up maintenance mode correctly:The server is temporarily unable to service your request due to maintenance downtime or capacity problems. Please try again later. - If necessary, update the development database again to get any final transactions processed by your current production system.
For details, see Updating the Magento Database. - Put your production system in maintenance mode so it cannot process orders.
- Make your development system live.
The way you do this is up to you; typically, you can configure your DNS server to send requests for your web store domain to the development system's IP address. Be aware that propagating the change to other DNS servers can take some time. - Verify your former development system is functioning as your new Magento web store in production.
- Shut down the old production system.
Congratulations! You successfully upgraded! Review our welcome page to see the improvements you're getting.
Setting Magento File System Permissions and Ownership After Upgrade
To secure your Magento installation after the upgrade, see After You Install Magento: Recommended File System Ownership and Privileges.
Troubleshooting
There is a known issue after upgrading to EE 1.13.1 that affects you only if you do not follow the recommended procedure to upgrade to a new environment as discussed in Getting Ready For Your Upgrade.
Symptom: After completing the upgrade, when you log in to the Admin Panel and click System > Configuration, a fatal error similar to the following displays in your browser:
Class 'Mage_Googlecheckout_Helper_Data' not found in /var/www/html/magento/app/Mage.php on line 547
Solution:
- Close the Admin Panel browser window.
- As a user with
rootprivileges, delete all files exceptconfig.xmlfrom the following directory:
[your Magento install dir]/app/code/core/Mage/GoogleCheckout/etc
- When you log back in to the Admin Panel, everything works as expected.
In the event of any other issue during the upgrade, see Getting Help With Your Installation or Upgrade.