Technical Details
This topic discusses technical implementation details about pipeline deployment in Magento 2.2 and later. Improvements can be divided into the following areas:
This topic also discusses the recommended workflow for pipeline deployment and provides some examples to help you understand how it works.
Before you get started, review the prerequisite for your development, build, and production systems.
Configuration management
To enable you to synchronize and maintain the configuration of your development and production systems, we use the following override scheme.
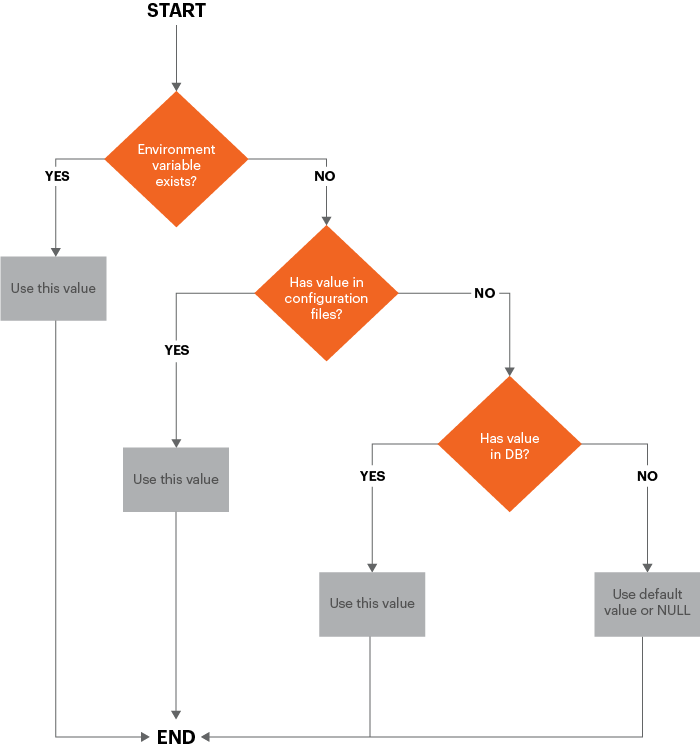
As the diagram shows, we get configuration values in the following order:
- Environment variables, if they exist, override all other values.
- From the shared configuration files
env.phpandconfig.php. Values inenv.phpoverride values inconfig.php. - From values stored in the database.
- If no value exists in any of those sources, we use either the default value or NULL.
Manage the shared configuration
The shared configuration is stored in app/etc/config.php, which should be in source control.
Set the shared configuration in the Magento Admin in your development (or Magento Commerce Cloud integration) system and write the configuration to config.php using the magento app:config:dump command.
Manage the system-specific configuration
The system-specific configuration is stored in app/config/env.php, which should not be in source control.
Set the system-specific configuration in the Magento Admin in your development (or Magento Commerce Cloud integration) system and write the configuration to env.php using the magento app:config:dump command.
This command also writes sensitive settings to env.php.
Manage the sensitive configuration
The sensitive configuration is also stored in app/etc/env.php.
You can manage the sensitive configuration in any of the following ways:
- Environment variables
- Save the sensitive configuration in
env.phpon your production system using themagento config:set:sensitivecommand
Configuration settings locked in the Magento Admin
Any configuration settings in config.php or env.php are locked in the Magento Admin; that is, those settings cannot be changed in the Admin.
Use the magento config:set or magento config:set --lock command to change the settings in the config.php or env.php files.
Changes in the Magento Admin
We changed the following behavior in the Magento Admin in production mode:
- You cannot enable or disable cache types in the Admin
-
Developer settings are unavailable (Stores > Settings > Configuration > Advanced > Developer), including:
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
- Merge CSS and JavaScript
- Server-side or client-side LESS compilation
- Inline translations
- As discussed previously, any configuration setting in
config.phporenv.phpis locked and cannot be edited in the Admin. - You can change the Admin locale only to languages used by deployed themes
The following figure shows an example of the Account Setting> Interface Locale list in the Admin showing only two deployed locales:
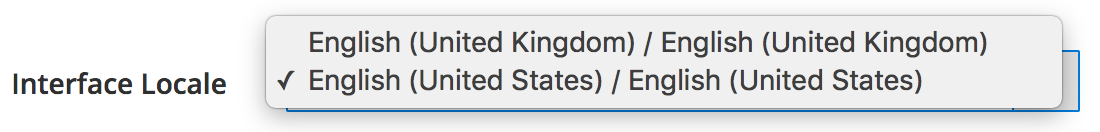
-
You cannot change locale configurations for any scope using the Admin Panel.
We recommend making these changes before switching to Production mode.
You can still configure the locale using environment variables or the config:set CLI command with the path
general/locale/code.
cron installation and removal
In version 2.2 for the first time, we help you set up your Magento cron job by providing the magento cron:install command. This command sets up a Magento crontab as the user who runs the command.
We also enable you to remove the Magento crontab using the magento cron:remove command.
Recommended pipeline deployment workflow
The following diagram shows how we recommend you use pipeline deployment to manage the configuration.
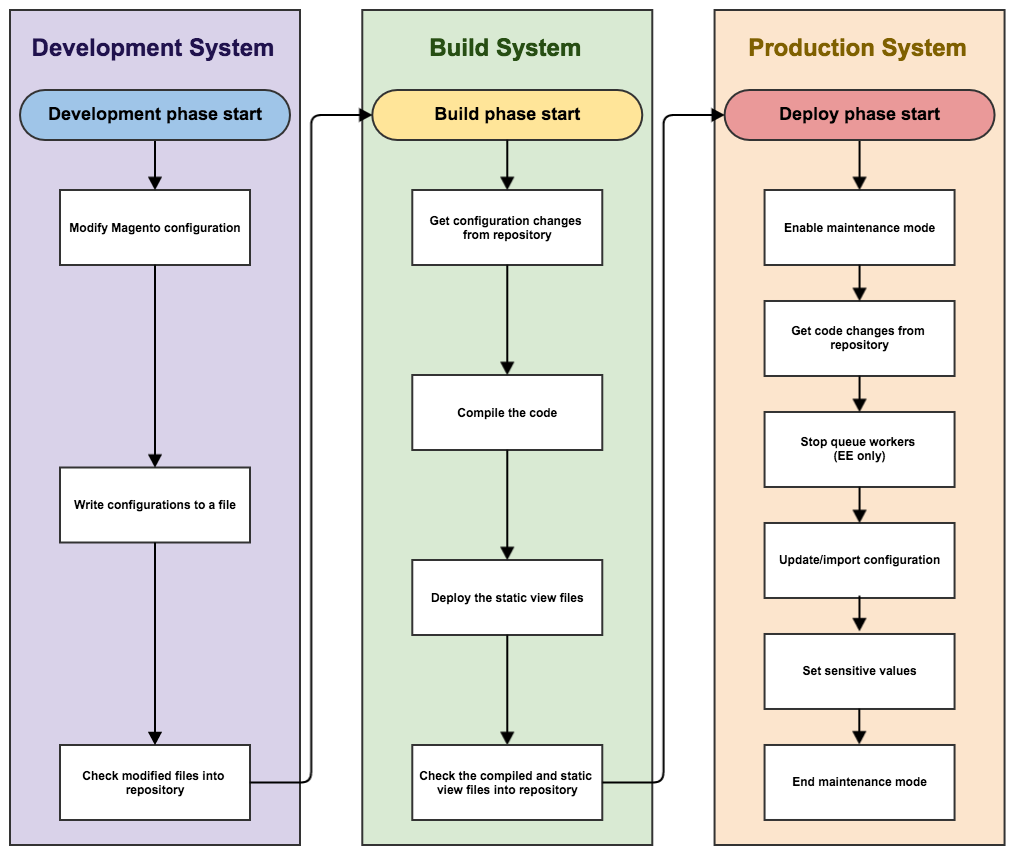
Development system
On your development system, you make configuration changes in the Magento Admin and generate the shared configuration, app/etc/config.php and the system-specific configuration, app/etc/env.php. Check Magento code and the shared configuration into source control and push it to the build server.
You should also install extensions and customize Magento code on the development system.
On your development system:
-
Set the configuration in the Magento Admin.
-
Use the
magento app:config:dumpcommand to write the configuration to the file system.app/etc/config.phpis the shared configuration, which contains all settings except sensitive and system-specific settings. This file should be in source control.app/etc/env.phpis the system-specific configuration, which contains settings that are unique to a particular system (for example, hostnames and port numbers). This file should not be in source control.
-
Add your modified code and the shared configuration to source control.
Build system
The build system compiles code and generates static view files for themes registered in Magento. It doesn’t need a connection to the Magento database; it needs only the Magento codebase.
On your build system:
- Pull the shared configuration file from source control.
- Use the
magento setup:di:compilecommand to compile code. - Use the
magento setup:static-content:deploy -fcommand to update static file view files. - Check the updates into source control.
Production system
On your production system (that is, your live store) you pull generated assets and code updates from source control and set system-specific and sensitive configuration settings using the command line or environment variables.
On your production system:
- Start maintenance mode.
- Pull code and configuration updates from source control.
- If you use Magento Commerce, stop queue workers.
- Use the
magento app:config:importcommand to import configuration changes in the production system. - If you installed components that changed the database schema, run
magento setup:upgrade --keep-generatedto update the database schema and data, preserving generated static files. - To set system-specific settings, use either the
magento config:setcommand or environment variables. - To set sensitive settings, use either the
magento config:sensitive:setcommand or environment variables. - Clean (also referred to as flush) the Magento cache.
- End maintenance mode.
Configuration management commands
We provide the following commands to help you manage the configuration:
magento app:config:dumpto write Magento Admin configuration settings toconfig.phpandenv.php(except for sensitive settings)-
magento config:setto set the values of system-specific settings on the production system.Use the optional
--lockoption to lock the option in the Magento Admin (that is, make the setting uneditable). If a setting is already locked, use the--lockoption to change the setting. magento config:sensitive:setto set the values of sensitive settings on the production system.magento app:config:importto import configuration changes fromconfig.phpandenv.phpto the production system.
Configuration management examples
This section shows examples of managing the configuration so you can see how changes are made to config.php and env.php.
Change the default locale
This section shows the change made to config.php when you change the default weight unit using the Magento Admin (Stores > Settings > Configuration > General > General > Locale Options).
After you make the change in the Admin, run bin/magento app:config:dump to write the value to config.php. The value is written to the general array under locale as the following snippet from config.php shows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
'general' =>
array (
'locale' =>
array (
'code' => 'en_US',
'timezone' => 'America/Chicago',
'weight_unit' => 'kgs'
)
)
Change several configuration settings
This section discusses making the following configuration changes:
- Adding a website, store, and store view (Stores > Settings > All Stores)
- Changing the default email domain (Stores > Settings > Configuration > Customers > Customer Configuration)
- Setting the PayPal API Username and API password (Stores > Settings > Configuration > Sales > Payment Methods > PayPal > Required PayPal Settings)
After you make the change in the Admin, run bin/magento app:config:dump on your development system. This time, not all of your changes are written to config.php; in fact, only the website, store, and store view are written to that file as the following snippets show.
config.php
config.php contains:
- Changes to the website, store, and store view.
- Non-system-specific Elasticsearch settings
- Non-sensitive PayPal settings
- Comments that inform you of sensitive settings that were omitted from
config.php
websites array:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
'new' =>
array (
'website_id' => '2',
'code' => 'new',
'name' => 'New website',
'sort_order' => '0',
'default_group_id' => '2',
'is_default' => '0',
),
groups array:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2 =>
array (
'group_id' => '2',
'website_id' => '2',
'code' => 'newstore',
'name' => 'New store',
'root_category_id' => '2',
'default_store_id' => '2',
),
stores array:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
'newview' =>
array (
'store_id' => '2',
'code' => 'newview',
'website_id' => '2',
'group_id' => '2',
'name' => 'New store view',
'sort_order' => '0',
'is_active' => '1',
),
payment array:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
'payment' =>
array (
'paypal_express' =>
array (
'active' => '0',
'in_context' => '0',
'title' => 'PayPal Express Checkout',
'sort_order' => NULL,
'payment_action' => 'Authorization',
'visible_on_product' => '1',
'visible_on_cart' => '1',
'allowspecific' => '0',
'verify_peer' => '1',
'line_items_enabled' => '1',
'transfer_shipping_options' => '0',
'solution_type' => 'Mark',
'require_billing_address' => '0',
'allow_ba_signup' => 'never',
'skip_order_review_step' => '1',
),
env.php:
The default email domain system-specific configuration setting is written to app/etc/env.php.
The PayPal settings are written to neither file because the magento app:config:dump command does not write sensitive settings. You must set the PayPal settings on the production system using the following commands:
1
bin/magento config:sensitive:set paypal/wpp/api_username <username>
1
bin/magento config:sensitive:set paypal/wpp/api_password <password>
Prerequisite for your development, build, and production systems
File permissions and ownership must be consistent across development, build, and production systems. To make this work, you must either:
-
All of the following:
- Set up the same Magento file system owner username on all systems
- Make sure the web server runs as the same user on all systems
- Make sure the Magento file system owner is in the web server group on all systems
-
Change Magento file system permissions and ownership on each system as necessary using the following guidelines:
- Development and build: Set pre-installation ownership and permissions (two users)
- Production: Magento ownership and permissions in development and production
If you choose this approach, you must set file system permissions and ownership every time you pull code from your build system (if the Magento file system owner or web server user are different on your build system).
Related topics
- For a complete list of system-specific and sensitive settings and corresponding configuration paths, see Sensitive and system-specific configuration paths reference.
- config.php reference for detailed information about the shared configuration file
- env.php reference for detailed information about the system-specific configuration file
Next steps