Scaled architecture
The Cloud infrastructure scales according to your resource needs to achieve greater efficiency. The Magento Commerce Cloud monitors your applications and can adjust capacity to maintain steady, predictable performance. Converting to this architecture helps to mitigate problems, such as latency or large spikes in traffic.
The scaled architecture is available for Magento Commerce Cloud accounts with the Pro48 cluster or greater.
Split architecture
Historically, the Pro architecture consisted of 3 nodes, each containing a full tech stack. Now, there is a scalable infrastructure that provides a tiered solution with a minimum of 6 nodes: 3 nodes for the core database and other services and 3 nodes for the web server. This split architecture provides the capability to scale tiers independently to achieve an optimal balance of performance. The core tier scales vertically (increases in size), and the web tier scales horizontally (increases instance count) and vertically (changes instance type and size).
Scaling must use the same instance type and size for each node:
M5 or M5n instancesfor each core nodeC5 instancesfor each web node
Core tier scaling
There are 3 nodes (core nodes) for data storage, cache, and services: ElasticSearch, MariaDB, Redis, and more. When the core tier approaches capacity, the only way to scale is to increase the server size, such as boosting the CPU power and memory. Capacity is limited to the size of the node that is available. Because the database cluster is designed for high availability, you cannot scale horizontally in a reliable way with the technologies used.
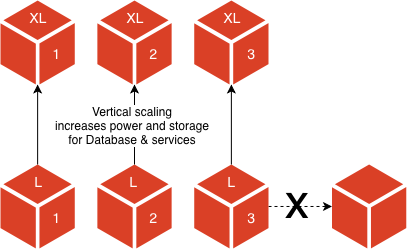
Consider an example that the core node instance type is m5.2xlarge with 32Gb RAM. A service, such as the database, uses a considerable amount of memory (30Gb). Scaling to the next available instance size m5.4xlarge provides 64Gb RAM, which doubles the memory and accommodates the growing needs of the database.
You can further optimize the performance of the core tier by routing traffic based on the node type. By default, the database node is isolated from the web traffic. As an example, you can choose to serve web traffic on the database node.
Web tier scaling
There are 3 nodes (web nodes) for processing requests and web traffic: php-fpm and NGINX. In addition to vertical scaling by increasing power and memory, the web tier can scale horizontally by adding extra web servers to an existing cluster when constricted at the PHP level.
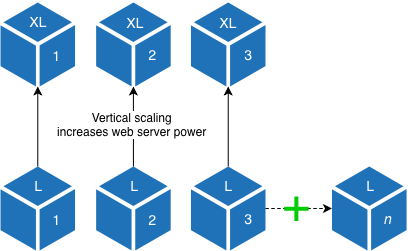
This complements the vertical scaling provided by the core tier. As the core tier scales in size and power to accommodate a growing database and increase in service usage, the web tier scales in size and power, and even instances, to accommodate an increase in process requests and higher traffic requirements.
Consider an example that the web node instance type is C5.2xlarge with 8 CPU and 16Gb RAM. The number of requests to the site increased greatly. You can add an additional C5.2xlarge node to handle the increase in php-fpm processes or you can change each instance type to C5.4xlarge with 16 CPU and 32Gb RAM. Adding an additional node reduces the risk of insufficient surge capacity.
Project structure
Minimally, Pro projects with the Scaled architecture have 6 nodes available.
- 3 web nodes c5.2xlarge (8 CPU, 16 Gb RAM)
- 3 core nodes m5.2xlarge (8 CPU, 32 Gb RAM)
Each project is unique, however, and requires performance monitoring to properly analyze resource management. Each account includes the New Relic Infrastructure service, which automatically connects with the application data and performance analytics to provide dynamic server monitoring. Specifically, you can use the New Relic service to monitor CPU and RAM utilization to determine which nodes require additional resources. As a resource reaches capacity or you notice a degradation in performance based on the analytics, you can create a request to scale your infrastructure to meet the demand.
SSH access
Certain files and logs, such as the /app/<project-id>/var/log directory, are not shared between nodes. Each node has a unique SSH access. You can not use the Magento Cloud CLI to log in to the core or web nodes, but you can find the node addresses in the SSH Access list in the Project Web UI.
1
ssh <node>.<project-ID>-<environment>-<user-ID>@ssh.<region>.magento.com
node1 to 3—Addresses to access the core nodesnode4 to n—Addresses to access the web nodes
After you log in, you can confirm the server ID and the role: core nodes use the unified role, and web nodes use the web role.
Example response as you log in to a core node includes the unified role:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
__ __ _ ___ _ _
| \/ |__ _ __ _ ___ _ _| |_ ___ / __| |___ _ _ __| |
| |\/| / _` / _` / -_) ' \ _/ _ \ | (__| / _ \ || / _` |
|_| |_\__,_\__, \___|_||_\__\___/ \___|_\___/\_,_\__,_|
|___/
Welcome to Magento Cloud.
This is server unique-server-id, role project-id:unified.
project-id@server-id:~$
Example response as you log in to a web node includes the web role:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
__ __ _ ___ _ _
| \/ |__ _ __ _ ___ _ _| |_ ___ / __| |___ _ _ __| |
| |\/| / _` / _` / -_) ' \ _/ _ \ | (__| / _ \ || / _` |
|_| |_\__,_\__, \___|_||_\__\___/ \___|_\___/\_,_\__,_|
|___/
Welcome to Magento Cloud.
This is server unique-server-id, role project-id:web.
project-id@server-id:~$
Log locations
The log locations vary slightly depending on the node. For example, a database log, such as the MySQL error log, is available on a core node (/var/log/mysql/mysql-error.log), but it is not available on a web node.