Configuration management for store settings
Configuration management provides a way to deploy across your environments with minimal downtime using Pipeline deployment. Magento Commerce Cloud provides the build server, build and deploy scripts, and deployment environments.
You must have environment-level, Admin role privileges to complete configuration management tasks.
Consistent configuration
The database contains default configurations for your Magento store. When you update configurations in the Magento Commerce Cloud environments using the Magento Admin panel, your configuration changes apply to the app/etc/config.php file. You can then use this file to manage and synchronize the Magento application configuration for your local environment and across each Cloud environment.
Use the ece-tools command in the remote environment to generate a config.php file:
1
./vendor/bin/ece-tools config:dump
The data “dumped” to the app/etc/config.php file becomes locked, which means the corresponding field in the Magento Admin panel becomes read-only. The config.php file includes only the settings that you configure. It does not lock the default values. Locking only the values you update also ensures that all extensions used in the Staging and Production environments do not break due to read-only configurations, especially Fastly.
Configuration data
System settings refer to the configurations in the Magento Admin Stores > Settings > Configuration section.
The app/etc/config.php file includes system configuration settings for stores, websites, modules or extensions, static file optimization, and system values related to static content deployment.
The config.php file includes the following settings and configuration values:
- Configured values for settings entered through the Magento Admin store configuration
- Extension list
- Scopes value for static content deployment (the default SCD strategy is quick)
The ece-tools config:dump command does not retrieve detailed configurations for modules, such as B2B. If you need a comprehensive configuration dump, use the Magento app:config:dump command, but be aware that this command locks configuration values in a read-only state.
Because Magento Commerce Cloud supports only the Magento production and maintenance modes, the Advanced > Developer section is not accessible in the Admin panel. You can configure additional settings using environment variables.
Sensitive data
Sensitive values are not stored in the app/etc/config.php file. Any sensitive configurations export to the app/etc/config.php file during the config:dump process. We recommend using environment variables to store sensitive values. For an example, see Add Magento authentication keys.
SCD performance
Depending on the size of your store, you may have a large amount of static content files to deploy. Normally, static content deploys during the deploy phase when Magento is in Maintenance mode. The most optimal configuration is to generate static content during the build phase. See Choosing a deploy strategy.
Before deploying static files, the build and deploy phases compress static content using GZIP. Compressing static files reduces server loads and increases site performance. Refer to Magento build options to learn about customizing or disabling file compression.
Configuration logic flow
All system configurations are set during build and deploy according to the following override scheme:
- If an environment variable exists, use the custom configuration and ignore the default configuration.
- If an environment variable does not exist, use the configuration from a
MAGENTO_CLOUD_RELATIONSHIPSname-value pair in the.magento.app.yamlfile. Ignore the default configuration. - If an environment variable does not exist and
MAGENTO_CLOUD_RELATIONSHIPSdoes not contain a name-value pair, remove all customized configuration and use the values from the default configuration.
Procedure to manage your settings
The following illustrates a high-level overview of this process:
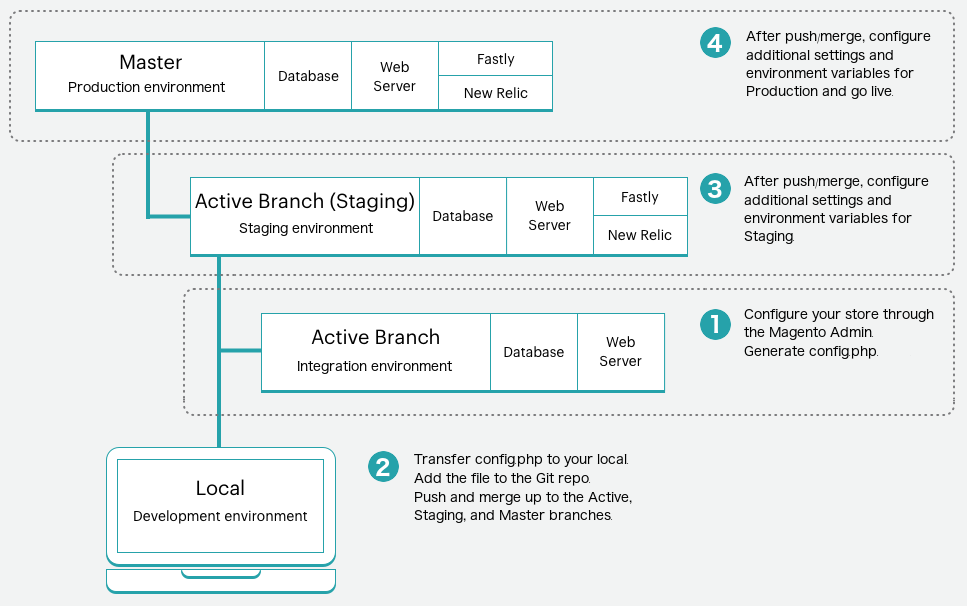
To configure your store and generate a configuration file:
-
Complete all configurations for your stores in the Admin panel for one of the environments:
- Starter: An active development branch
- Pro: Integration environment
These configurations do not include the actual products unless you plan on dumping the database from this environment to Staging and Production environments. Typically, development databases do not include your full store data.
-
On your local workstation, change to the Cloud project root directory.
-
Use SSH to log in to the remote environment and generate the
/app/etc/config.phpfile.1
ssh <SSH-URL> "./vendor/bin/ece-tools config:dump"
To transfer the configuration file and apply to another environment:
-
On your local workstation, change to the Cloud project root directory.
-
Transfer the
/app/etc/config.phpfile to your local project folder usingrsyncorscp.1
rsync <SSH-URL>:app/etc/config.php ./app/etc/config.php
-
Add, commit, and push code changes to update a remote environment.
1
git add app/etc/config.php
1
git commit -m "Add system-specific configuration"
1
git push origin <branch-name>
After the deployment is complete, log in to the Magento Admin panel for the updated environment to verify the settings. Continue to merge any additional configurations to the Staging and Production environments, as needed.
Update configurations
When you modify your environment through the Magento Admin panel and run the command again, new configurations are appended to the code in the config.php file.
While you can manually edit the config.php file in the Staging and Production environments, we do not recommend it. The file helps to keep all configurations consistent across all environments. Never delete the config.php file to rebuild it. Deleting the file can remove specific configurations and settings required for build and deploy processes.
Migrate older configurations
If you upgrade to Magento Commerce Cloud 2.2 or later, you may want to migrate settings from the config.local.php file to your new config.php file. If the configuration settings in your Magento Admin panel match the contents of the file, follow the instructions to generate and add the config.php file.
If they differ, you can append content from the config.local.php file to your new config.php file:
-
Follow instructions to generate the
config.phpfile. -
Open the
config.phpfile and delete the last line. -
Open the
config.local.phpfile and copy the contents. -
Paste the contents into the
config.phpfile, save, and complete adding it to Git. -
Deploy across your environments.
You only need to complete this migration once. When you need to update the file, always update the config.php file.
Change locales
You can change your store locales without following a complex configuration import and export process, if you have SCD_ON_DEMAND enabled. You can update the locales using the Admin panel.
You can add another locale to the Staging or Production environment by enabling SCD_ON_DEMAND in an Integration branch, generate an updated config.php file with the new locale information, and copy the configuration file to the target environment.
This process overwrites the store configuration; only do the following if the environments contain the same stores.
-
In the Integration environment, enable the
SCD_ON_DEMANDvariable using the.magento.env.yamlfile. -
Add the necessary locales using your Admin panel.
-
Use SSH to log in to the remote environment and generate the
/app/etc/config.phpfile containing all locales.1
ssh <SSH-URL> "./vendor/bin/ece-tools config:dump" -
Copy the new configuration file from your Integration environment to your local environment directory.
1
rsync <SSH-URL>:app/etc/config.php ./app/etc/config.php
-
Add, commit, and push code changes to update a remote environment.